STATIONARY MULTI-USE
AND SINGLE USE NPWT:
RECOMMENDATIONS OF AN EXPERT PANEL
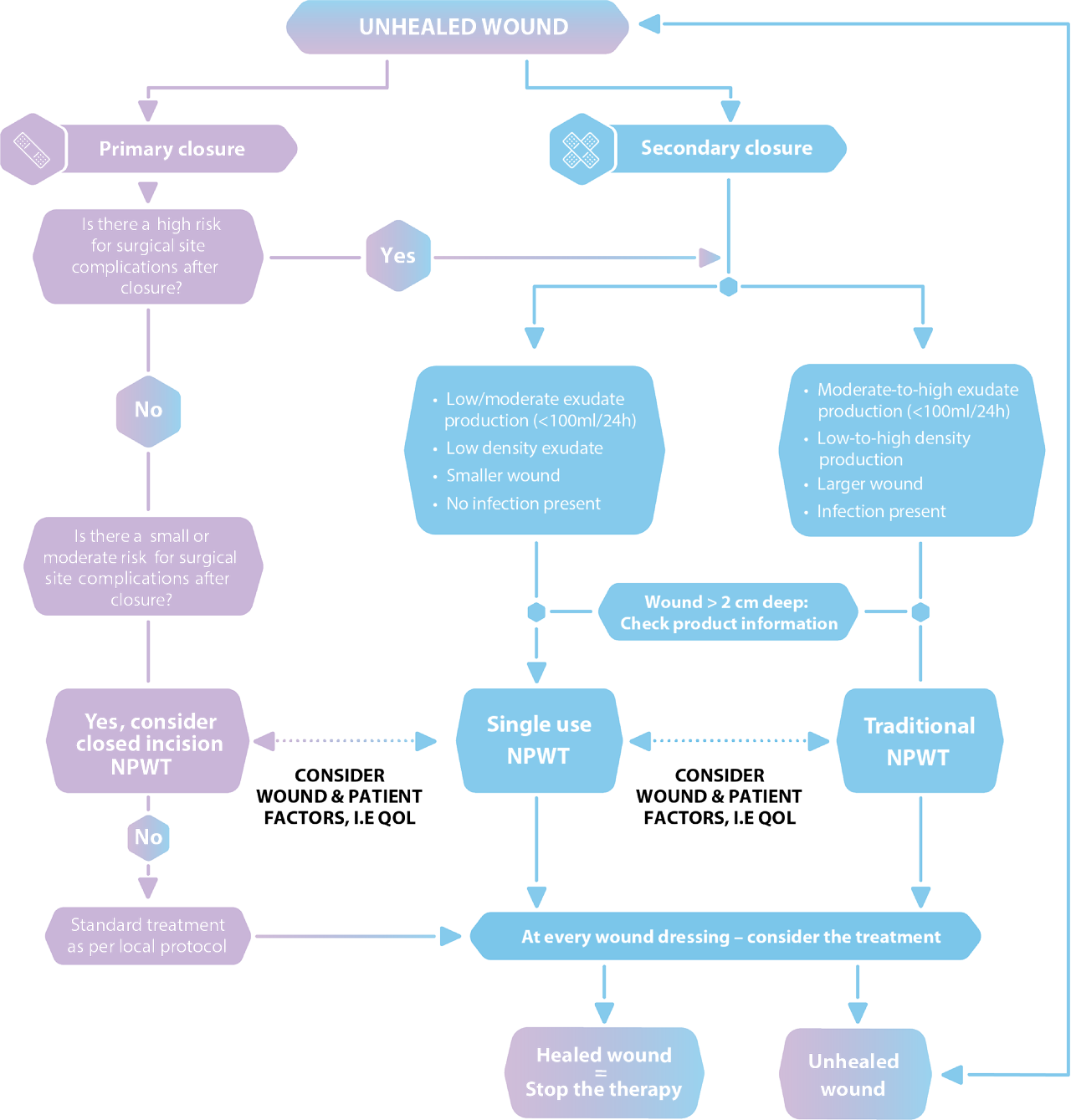
Negative pressure wound therapy (NPWT) is a concept that has been around for over 20 years. There is now more choice, potential and possibilities for the use of the NPWT for different indications. An international group of specialist surgeons with a high level of experience of NPWT in various wound types convened to discuss the use of NPWT today.